Type Casting
Java Type Casting
Type casting is when you assign a value of one primitive data type to another type.
In Java, there are two types of casting:
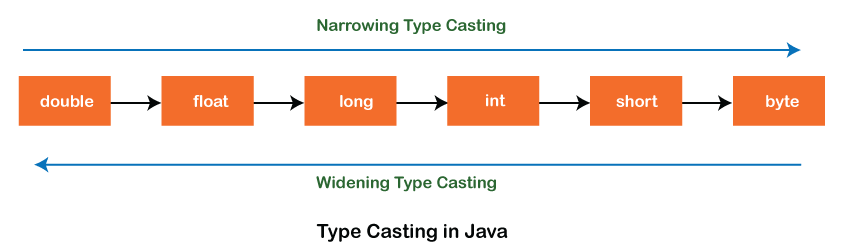
- Widening Casting (automatically) - converting a smaller type to a larger type size
byte->short->char->int->long->float->double - Narrowing Casting (manually) - converting a larger type to a smaller size type
double->float->long->int->char->short->byte
Widening Casting
Widening casting is done automatically when passing a smaller size type to a larger size type:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int myInt = 9;
double myDouble = myInt; // Automatic casting: int to double
System.out.println(myInt); // Outputs 9
System.out.println(myDouble); // Outputs 9.0
}
}
Narrowing Casting
Narrowing casting must be done manually by placing the type in parentheses () in front of the value:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double myDouble = 9.78;
int myInt = (int) myDouble; // Manual casting: double to int
System.out.println(myDouble); // Outputs 9.78
System.out.println(myInt); // Outputs 9
}
}
Comments
Post a Comment